Testicular Cancer
Most commonly occurs in younger men age 15-45 but can present later in life.
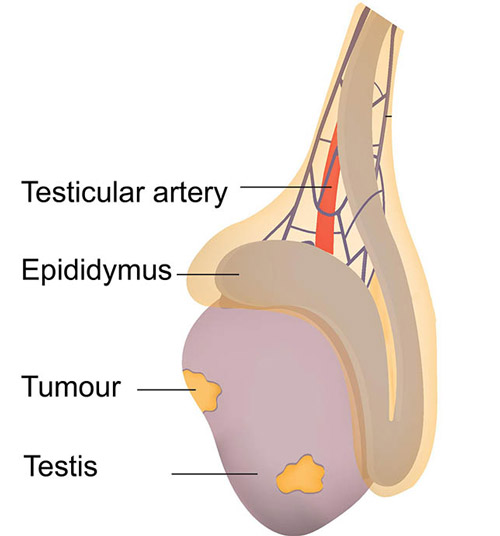
Cancer of the testicle usually presents in one testicle only. A normal testicle feels spongy, when a cancer develops this usually presents as painless hard lump.
Testicular cancer most commonly occurs in younger men between the age 15-45 but can also present later in life, on average men wait 5 months before seeking help.
Most testicular cancers are curable even if spread outside the testicle (metastatic).
Screening for
Testicular Cancer
An ultrasound of the testicle is performed to assist diagnosis, blood tests and a CT scan are also usually requested.

Treatment
Testicular cancer is highly treatable and usually curable. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or stem cell transplantation. Even in cases in which cancer has spread widely, chemotherapy offers a cure rate greater than 80%.
Surgical removal of the affected testicle is performed which is usually an overnight stay in hospital. the incision is made in the lower abdomen (like a hernia).
A prosthesis (artificial testicle) can be implanted at the same time if desired.
Further treatment depends on the type and stage (how advanced) the tumour is.




